支持间质细胞瘤
| 支持间质细胞瘤 | |
|---|---|
| 分类系统及外部资源 | |
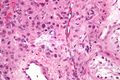
 显微镜下的支持间质细胞瘤。间质细胞有大量嗜酸性和淡粉色的细胞质;支持细胞有淡白色或无色的细胞质。 | |
| ICD-9 | 183.0, 256.1 |
| ICD-O: | 8630-8631/0 |
| MedlinePlus | 001172 |
| MeSH | D018310 |
支持间质细胞瘤(Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour),是一类肿瘤包含不同数量的支持细胞、间质细胞,一些情况下也包括少量不同肿瘤、原始性索基质和异种物质。
支持间质细胞瘤是一种隶属于卵巢肿瘤或睾丸肿瘤下的一类性索间质肿瘤[1]。这种疾病非常罕见,少于1%的睾丸肿瘤。肿瘤可能发生于任何年龄段,但主要以青年人为主。
最近研究显示一些卵巢支持间质细胞瘤是由DICER1基因的生殖细胞突变而产生[2][3]。这些遗传性案例逐渐年轻化,并常伴有多结节性甲状腺肿,一些其他罕见肿瘤均有个人或家族的病史,包括胸膜肺母细胞瘤、肾母细胞瘤和宫颈横纹肌肉瘤。
在医学主题词表中,男性细胞瘤(arrhenoblastoma)[4]和男性母细胞瘤(androblastoma)[5],均被定义归类于支持间质细胞瘤。
目录 |
分类
支持间质细胞瘤被分为许多子类,最典型的是由支持细胞组成的小管链接间质细胞组成的间质集群。
特征
由于肿瘤产生过度的睾丸激素,1/3的女性患者都有伴有一定情况的男性化。男性化过程之前,病人会出现停止排卵、月经过少、闭经及失雌性态。其他症状包括有寻常痤疮、多毛症、声音变粗、阴蒂肥大、颞发衰退和肌肉组织增强等。此外睾丸内睾酮指数很高。
诊断
出现卵巢肿瘤并伴有内分泌障碍情况则可推测为支持间质细胞瘤;但是,内分泌紊乱症状在间质细胞瘤中只占有2/3的病例。所以,必须通过术中及术后的病理分析,才能做出最终的确定诊断。
治疗
最常见的方法是采取手术。对于卵巢支持间质细胞瘤的手术通常是保留生育功能的单侧输卵管卵巢切除术。对于恶性肿瘤,需要采用更激进的手术策略,并通常使用辅助化学疗法,一些时候需要放射疗法。在所有治疗过程中,需要保持多次物理检查与成像监控,因为在很多病例中,支持间质细胞瘤并没有引起肿瘤标记数值的增加[6]。由于一些支持间质细胞瘤有遗传性,所以建议进行临床遗传学服务工作。
预后效果通常很理想,肿瘤大多时候生长缓慢,而且是良性的[7]。但对于恶性肿瘤的病例,因为其组织学不同,预后效果往往很差[6]。
图像
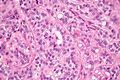
高度显微镜下的间质细胞瘤 | 高度显微镜下的支持细胞瘤 |
相关
参考
- ↑ Sachdeva, Poonam; Arora, Raksha; Dubey, Chandan; Sukhija, Astha; Daga, Mridula; Kumar Singh, Deepak. Sertoli–Leydig cell tumor: A rare ovarian neoplasm. Case report and review of literature. Gynecological Endocrinology. 2008, 24 (4): 230–4. doi:10.1080/09513590801953465. PMID 18382911.
- ↑ Frio, Thomas Rio; Bahubeshi, Amin; Kanellopoulou, Chryssa; Hamel, Nancy; Niedziela, Marek; Sabbaghian, Nelly; Pouchet, Carly; Gilbert, Lucy et al.. DICER1 Mutations in Familial Multinodular Goiter With and Without Ovarian Sertoli-Leydig Cell Tumors. JAMA. 2011, 305 (1): 68–77. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1910. PMID 21205968.
- ↑ Slade, Ingrid; Bacchelli, Chiara; Davies, Helen; Murray, Anne; Abbaszadeh, Fatemeh; Hanks, Sandra; Barfoot, Rita; Burke, Amos et al.. DICER1 syndrome: clarifying the diagnosis, clinical features and management implications of a pleiotropic tumour predisposition syndrome. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2011, 48 (4): 273–8. doi:10.1136/jmg.2010.083790. PMID 21266384.
- ↑ 道兰氏医学词典中的arrhenoblastoma
- ↑ 道兰氏医学词典中的androblastoma
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lenhard M, Kuemper C, Ditsch N, Diebold J, Stieber P, Friese K, Burges A. Use of novel serum markers in clinical follow-up of Sertoli-Leydig cell tumours. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med.. 2007, 45 (5): 657–61. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2007.120. PMID 17484630.
- ↑ Al-Agha OM, Axiotis CA. An in-depth look at Leydig cell tumor of the testis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med.. February 2007, 131 (2): 311–7. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2007)131[311:AILALC]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17284120.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||