Riboflavin kinase
核黄素激酶 |
|---|
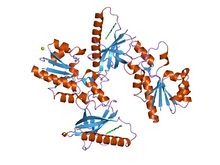 |
| crystal structure of flavin binding to fad synthetase from thermotoga maritina |
| 鉴定 |
|---|
| 标志 | Flavokinase |
|---|
| Pfam(蛋白家族查询站) | PF01687 |
|---|
| InterPro(蛋白数据整合站) | IPR015865 |
|---|
| SCOP(蛋白结构分类数据站) | 1mrz |
|---|
|
Riboflavin kinase
核黄素激酶 |
|---|
| 鉴定 |
|---|
| 标志 | Riboflavin_kinase |
|---|
| Pfam(蛋白家族查询站) | PF01687 |
|---|
| InterPro(蛋白数据整合站) | IPR015865 |
|---|
|
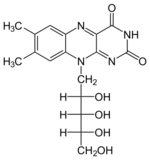
核黄素激酶(英语:riboflavin kinase,EC 2.7.1.26)是一个催化以下化学反应的酶:
- ATP + 核黄素
 ADP + FMN
ADP + FMN
该酶催化的反应的底物为ATP和核黄素,产物是ADP和黄素单核苷酸(FMN)。
但是,在古菌核黄素激酶(EC 2.7.1.161)中,常使用CTP而非ATP作为反应底物,催化如下反应:
- CTP + 核黄素
 CDP + FMN [2]
CDP + FMN [2]
核黄素激酶也在许多细菌中发现,具有类似的功能,但存在若干数量的氨基酸不同。
反应
 + XTP →
+ XTP → 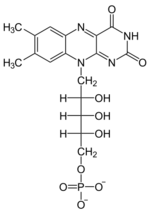 + XDP
+ XDP
Riboflavin is converted into catalytically active cofactors (FAD and FMN) by the actions of riboflavin kinase (EC 2.7.1.26), which converts it into FMN, and FAD synthetase (EC 2.7.7.2), which adenylates FMN to FAD. Eukaryotes usually have two separate enzymes, while most prokaryotes have a single bifunctional protein that can carry out both catalyses, although exceptions occur in both cases. While eukaryotic monofunctional riboflavin kinase is orthologous to the bifunctional prokaryotic enzyme,[3] the monofunctional FAD synthetase differs from its prokaryotic counterpart, and is instead related to the PAPS-reductase family.[4] The bacterial FAD synthetase that is part of the bifunctional enzyme has remote similarity to nucleotidyl transferases and, hence, it may be involved in the adenylylation reaction of FAD synthetases.[5]
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific, those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferases) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:riboflavin 5'-phosphotransferase. This enzyme is also called flavokinase. This enzyme participates in riboflavin metabolism.
结构
截止2007年底,这类酶中已有14个三级结构被解决,在PDB的登陆代码为1N05,1N06,1N07,1N08,1NB0,1NB9,1P4M,1Q9S,2P3M,2VBS,2VBT,3CTA,2VBU,2VBV。
参考文献
- ↑ PDB 3CTA; Bonanno, J.B., Rutter, M., Bain, K.T., Mendoza, M., Romero, R., Smith, D., Wasserman, S., Sauder, J.M., Burley, S.K., Almo, S.C.. Crystal structure of riboflavin kinase from Thermoplasma acidophilum. 2008.
- ↑ Ammelburg M, Hartmann MD, Djuranovic S, Alva V, Koretke KK, Martin J, Sauer G, Truffault V, Zeth K, Lupas AN, Coles M. A CTP-Dependent Archaeal Riboflavin Kinase Forms a Bridge in the Evolution of Cradle-Loop Barrels. Structure.. 2007, 12 (12): 1577–90. doi:10.1016/j.str.2007.09.027. PMID 18073108.
- ↑ Osterman AL, Zhang H, Zhou Q, Karthikeyan S. Ligand binding-induced conformational changes in riboflavin kinase: structural basis for the ordered mechanism. Biochemistry. 2003, 42 (43): 12532–8. doi:10.1021/bi035450t. PMID 14580199.
- ↑ Galluccio M, Brizio C, Torchetti EM, Ferranti P, Gianazza E, Indiveri C, Barile M. Over-expression in Escherichia coli, purification and characterization of isoform 2 of human FAD synthetase. Protein Expr. Purif.. 2007, 52 (1): 175–81. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2006.09.002. PMID 17049878.
- ↑ Srinivasan N, Krupa A, Sandhya K, Jonnalagadda S. A conserved domain in prokaryotic bifunctional FAD synthetases can potentially catalyze nucleotide transfer. Trends Biochem. Sci.. 2003, 28 (1): 9–12. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(02)00009-9. PMID 12517446.
延伸阅读
- CHASSY BM, ARSENIS C, MCCORMICK DB. THE EFFECT OF THE LENGTH OF THE SIDE CHAIN OF FLAVINS ON REACTIVITY WITH FLAVOKINASE. J. Biol. Chem.. 1965, 240: 1338–40. PMID 14284745.
- GIRI KV, KRISHNASWAMY PR, RAO NA. [http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1196627/ Studies on plant flavokinase]. Biochem. J.. 1958, 70 (1): 66–71. PMID 13584303. PMC 1196627.
- KEARNEY EB. The interaction of yeast flavokinase with riboflavin analogues. J. Biol. Chem.. 1952, 194 (2): 747–54. PMID 14927668.
- McCormick DB and Butler RC. Substrate specificity of liver flavokinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1962, 65 (2): 326–332. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(62)91051-X.
- Sandoval FJ, Roje S. An FMN hydrolase is fused to a riboflavin kinase homolog in plants. J. Biol. Chem.. 2005, 280 (46): 38337–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500350200. PMID 16183635.
- Solovieva IM, Tarasov KV, Perumov DA. Main physicochemical features of monofunctional flavokinase from Bacillus subtilis. B. Mosc, Biochemistry. (2): 177–81. PMID 12693963.
- Solovieva IM, Kreneva RA, Leak DJ, Perumov DA. The ribR gene encodes a monofunctional riboflavin kinase which is involved in regulation of the Bacillus subtilis riboflavin operon. Microbiology.. Pt 1, 145: 67–73. doi:10.1099/13500872-145-1-67. PMID 10206712.
|
|
|---|
| | 脂溶性维生素类 |
|
| |
|---|
| |
| α-生育酚转运蛋白 |
|---|
| |
| 肝脏(固醇27-羟化酶或CYP27A1) · 肾脏(25-羟维生素D3 1-α-羟化酶或CYP27B1) · 降解(1,25-二羟维生素D3 24-羟化酶或CYP24A1) |
|---|
| |
| 维生素K环氧化物还原酶 |
|---|
|
|---|
| | 水溶性维生素类 |
|
| 硫胺素二磷酸激酶 |
|---|
| |
| 吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶 · 甲酰胺酶 |
|---|
| |
| 泛酸激酶 |
|---|
| |
| 二氢叶酸合酶 · 二氢叶酸还原酶 · 丝氨酸羟甲基转移酶亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶 |
|---|
| |
| MMAA · MMAB · MMACHC · MMADHC |
|---|
| |
| L-古洛糖酸内酯氧化酶 |
|---|
| |
| 核黄素激酶 |
|---|
|
|---|
| | 非维生素辅因子类 |
|
|
GTP环水解酶Ⅰ · 6-丙酮酰四氢蝶呤合酶 · 墨蝶蛉还原酶
PCBD1 · PTS · QDPR |
|---|
| 钼辅因子
| MOCS1 · MOCS2 · MOCS3 · GPHN |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| 2.7.1-2.7.4:磷酸转移酶类/激酶
(PO4) |
| 2.7.1:以羟基为受体 |
- 己糖-
- 葡萄糖-
- 果-
- 半乳糖-
- 磷酸果糖-
- 核黄素
- 莽草酸
- 胸苷
- NAD+
- 甘油
- 泛酸
- 甲羟戊酸
- 丙酮酸
- 脱氧胞苷
- PFP
- 二酰甘油
- 磷酸肌醇 3
- 鞘氨醇
- 葡萄糖-1,6-二磷酸合酶
|
|---|
| | 2.7.2:以羧基为受体 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.3:以含氮基团为受体 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.4:以磷酸基团为受体 |
- 磷酸甲羟戊酸
- 腺苷酸
- 核苷二磷酸
- 尿苷酸
- 鸟苷酸
- 硫胺素二磷酸
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | 2.7.6:二磷酸转移酶类 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.7:核苷酸基转移酶 |
| 聚合酶 |
|
|---|
| 磷酸解作用
由3'端至5'端的核糖核酸外切酶 | |
|---|
| | 尿苷酰转移酶 |
- 葡萄糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰基转移酶
- 半乳糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰基转移酶
|
|---|
| | 鸟苷酰转移酶 | |
|---|
| | 其它 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | 2.7.8:杂项 |
| 磷脂酰基转移酶类 |
- CDP-甘油二酯—甘油-3-磷酸3-磷脂酰基转移酶
- CDP-甘油二酯—丝氨酸O-磷脂酰基转移酶
- CDP-甘油二酯—肌醇3-磷脂酰基转移酶
- CDP-甘油二酯—胆碱O-磷脂酰基转移酶
|
|---|
| | 糖基-1-磷酸转移酶类 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| 2.7.10-2.7.13:蛋白激酶类
(PO4;蛋白质受体) |
| 2.7.10:蛋白酪氨酸 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.11:蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.12:蛋白双特异性 | |
|---|
| | 2.7.13:蛋白组氨酸 | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
此条目包含有源于Pfam以及InterPro的属于公有领域的文本 IPR015865
参考来源
3个分类: 需要图片的蛋白质页面 | EC 2.7.1 | 已知结构的酶

 ADP + FMN
ADP + FMN CDP + FMN [2]
CDP + FMN [2]

